NestJs
开始
创建项目
Nest命令行创建
npm i -g @nestjs/cli
nest new project-name
手动创建
npm i --save @nestjs/core @nestjs/common rxjs reflect-metadata
核心文件
app.module.ts 应用的根模块
app.controller.ts 具有单一路由的基本控制器
app.service.ts 具有单一方法的基本服务
app.controller.spec.ts 控制器的单元测试文件
main.ts 使用核心函数 NestFactory 创建 Nest 应用实例的应用入口文件
启动
npm run start:dev
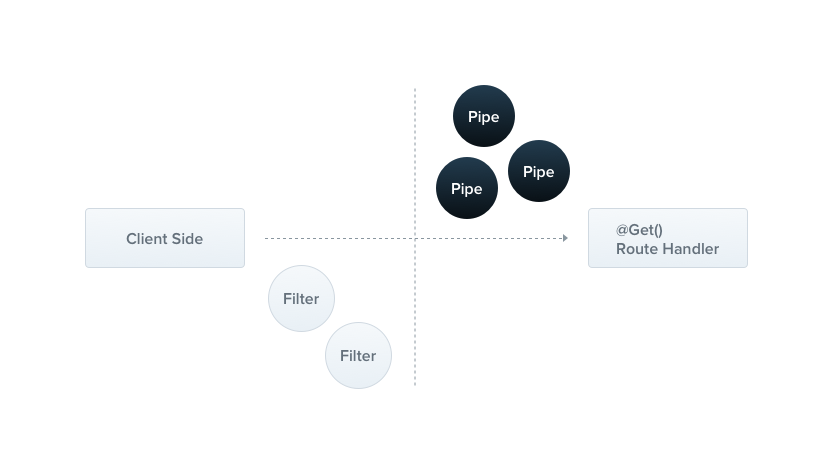
Controller
路由
控制器负责处理传入的 requests 并将 responses 返回给客户端,采用 routing 机制控制哪个控制器接收哪些请求
import { Controller, Get, Post } from '@nestjs/common';
import { AppService } from './app.service';
// 路由路径前缀,对路由分组
@Controller('article')
export class AppController {
constructor(private readonly appService: AppService) {}
@Get('one') // 请求方法装饰器为 HTTP 请求的特定端点创建处理程序
// /article/one
getArticle(): string {
return this.appService.getArticle();
}
@Post()
editArticle(): string {
return this.appService.editArticle();
}
}
请求方法
所有标准的HTTP 方法装饰器:@Get()、@Post()、@Put()、@Delete()、@Patch()、@Options() 和 @Head();
此外定义了一个 @All() 来处理所有HTTP 方法
路由通配符
路由路径支持正则的通配符匹配,如 @Get('article*')
子域路由
除了匹配路径的路由,支持host选项指定匹配主机的路由
@Controller({ host: 'xxx.example.com' })
export class AppController() {
@Get()
getData(): string { // 支持 @HostParam() 获取动态主机参数
// 子域路由处理
}
}
操作响应
默认nest根据请求处理返回数据的类型选择是否自动序列化,且 状态码 默认情况下始终为 200,可通过 @HttpCode() 装饰器自定义 ;
对于动态状态码,可通过使用库的响应对象上原生响应处理方法,以 express 为例:
@Get()
getArticle(@Res() response): void {
const data = this.appService.getArticle();
response.status(400).send(data)
}
请求对象
通过 @Req() 装饰器访问客户端 request 的详细信息
import { Controller, Get, Post, Req, Res } from '@nestjs/common';
import { AppService } from './app.service';
import { Request } from 'express';
@Controller('article')
export class AppController {
constructor(private readonly appService: AppService) {}
@Get('one')
getArticle(@Req() request: Request, @Res() response): void {
const data = this.appService.getArticle();
console.log(request)
response.status(400).send(data)
}
}
状态码
如前面所述,默认响应状态码 200(post为201),可通过装饰器 @HttpCode(code) 修改行为
@Post('list')
@HttpCode(200)
getList(){
...
}
响应头
使用装饰器 @Header() 或库的响应对象 res.header() 自定义响应头
@Post('login')
@Header('Cookie', 'xxxx')
login(){
...
}
重定向
使用装饰器 @Redirect 或库的响应对象 res.redirect() 响应重定向
@Post('login')
@Redirect('https://nest.nodejs.cn', 301)
路由参数
通过带参数的路由(动态路径)传参时,通过 @Param 装饰器访问
@Get('info/:id')
getInfo(@Param('id') id: string): string {
return `info: id is ${id}`
}
异步处理
采用异步处理让Nest解析延迟值
@Get()
async fingAll(): Promise<any[]> {
return [];
}
请求负载
通过 @Body() 装饰器接收POST路由参数,在此之前需要先使用class类或Ts接口声明DTO
// 推荐使用class类
const class CreateDTO {
name: string;
age: number;
}
@Post('create)
async create(@Body() createDTO: CreateDTO): string {
......
}
@Params(name): 提取路由参数
@Query(可选字段): 提取查询参数
@Body(可选字段): 提取请求体数据
特定库的响应对象
允许通过库的响应对象暴露API进行完全控制
import { Post, Res, HttpStatus } from '@nestjs/common';
import { Response } from 'express';
@Post()
create(@Res() res: Response) {
res.status(HttpStatus.CREATED).json([]);
}
这会失去Nest标准响应功能,可以设置响应头 passthrough 实现兼容
@Get()
findAll(@Res({ passthrough: true }) res: Response) {
res.status(HttpStatus.OK);
......
return [];
}
使用控制器类
声明的 Controller 类在 @Module() 装饰器的 controllers 将元数据附加到模块类
// 根模块类 app.module.ts
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { AppController } from './app.controller';
@Module({
controllers: [AppController], // 模块所需控制器
})
export class AppModule {}
Provider
NestJs中专于向其它对象提供功能并通过 injected 建立依赖关系的类,按功能可划分为服务、存储库、工厂、助手
基本使用
定义提供者 @Injectable
// article.service.ts
import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
import { Article } from "./interfaces/article.interface"
@Injectable()
export class ArticleService {
private readonly articles: Array<Article> = [];
createArticle(article: Article): Article {
this.articles.push(article)
return article;
}
getArticles(): Array<Article> {
return this.articles;
}
}
通过CLI命令 nest g service article 快速创建服务
定义类型
export interface Article {
name: string,
author: string,
pageTotal: number
}
定义DTO
export class CreateArticleDTO {
name: string;
author: string;
pageTotal: number
}
Controll中使用
// article.controller.ts
import { Controller, Get, Post, Body } from '@nestjs/common';
import { CreateArticleDTO } from "./dto/create-article.dto";
import {Article} from "./interfaces/article.interface"
import { ArticleService } from './article.service';
@Controller('article')
export class ArticleController {
// 类私有的实例属性
constructor(private readonly articleService: ArticleService) {
}
@Get('all')
async getArticles(): Promise<Array<Article>> {
return await this.articleService.getArticles();
}
@Post('create')
async createArticle(@Body() createArticleDTO: CreateArticleDTO): Promise<Article> {
return await this.articleService.createArticle(createArticleDTO)
}
}
依赖注入
Injectable 声明服务由IoC(控制反转)管理的类,通过依赖注入的设计模式很好地管理依赖;
具体实现:实现特定参数的构造函数,在新建对象时传入所依赖类型的对象
constructor(private catsService: CatsService) {} // 按类型解析
属性注入
当你的类多层拓展时
import { Injectable, Inject } from '@nestjs/common';
@Injectable()
export class HttpService<T> {
@Inject('HTTP_OPTIONS')
private readonly httpClient: T;
}
注册提供者
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { ArticleController } from './article/article.controller';
import { ArticleService } from './article/article.service';
// 应用根模块
@Module({
imports: [],
controllers: [ArticleController],
providers: [ArticleService], // 注册提供者
})
export class AppModule {}
模块
抽象功能模块,通过 @Module 供 Nest 用来组织应用结构的元数据(单个对象形式)
属性
providers: 可injectable实例化并支持模块内共享的程序
controllers: 需实例化的控制器集合
imports: Module所需的可提供程序模块列表
exports: Module被导入时提供的可用程序,如本身或者provide值
Module
基础使用
创建模块
// article/article.controller.ts
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { ArticleController } from './article.controller';
import { ArticleService } from './article.service';
@Module({
controllers: [ArticleController],
providers: [ArticleService],
})
export class ArticleModule {}
通过CLI命令 nest g module article 快速创建 module
导入模块
// app.module.ts
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { ArticleModule } from './article/article.module';
// 应用根模块
@Module({
imports: [ArticleModule],
})
export class AppModule {}
共享模块
任何导入了ArticleModule的模块将共享同一个实例
import {Module} from '@nestjs/common';
import {ArticleController} from './article.controller';
import {ArticleService} from './article.service';
@Module({
controllers: [ ArticleController ],
providers: [ArticleService],
exports: [ArticleService] // 导出
})
export class ArticleModule {}
模块导出
@Module({
imports: [CommonModule],
exports: [CommonModule],
})
export class CoreModule {}
依赖注入
@Module({
controllers: [CatsController],
providers: [CatsService],
})
export class CatsModule {
constructor(private catsService: CatsService) {}
}
全局模块
使用 @Global() 实现无需导入 imports 的全局可用模块,如助手、数据库连接
@Global()
@Module({
controllers: [ArticleController],
providers: [ArticleService],
exports: [ArticleService],
})
export class ArticleModule {}
Middleware
默认情况下,Nest 中间件等同于 express
Nest中使用中间件通过函数或 @Injectable() 装饰器的类实现
定义中间件
import { Injectable, NestMiddleware } from "@nestjs/common";
import { Request, Response, NextFunction } from "express";
@Injectable()
export class LoggerMiddleware implements NestMiddleware {
use(req: Request, res: Response, next: NextFunction) {
console.log('a request coming');
next();
}
}
应用中间件
import { MiddlewareConsumer,NestModule, Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { ArticleModule } from './article/article.module';
import { LoggerMiddleware } from "./middleware/logger.middleware";
@Module({
imports: [ArticleModule],
})
export class AppModule implements NestModule {
configure(consumer: MiddlewareConsumer){
consumer
.apply(LoggerMiddleware) // 支持依次传入多个中间件
.forRoutes('*') // 服务于路由,此处使用通配符匹配所有路径
}
}
限制到特定请求方法
import { RequestMethod, MiddlewareConsumer } from '@nestjs/common';
configure(consumer: MiddlewareConsumer) {
consumer
.apply(LoggerMiddleware)
.forRoutes({ path: 'cats', method: RequestMethod.GET });
}
依赖注入
import { Injectable, NestMiddleware } from '@nestjs/common';
import { Request, Response, NextFunction } from 'express';
@Injectable()
export class LoggerService {
log(message: string) {
console.log(message);
}
}
@Injectable()
export class LoggerMiddleware implements NestMiddleware {
constructor(private readonly loggerService: LoggerService) {}
use(req: Request, res: Response, next: NextFunction) {
this.loggerService.log('Middleware logging...');
next();
}
}
MiddlewareConsumer
中间件消费者,提供内置方法并以链式调用(chained)的管理中间件辅助类
forRoutes
若干字符串、一个 RouteInfo 对象、若干控制器类,forRoutes(ArticleController)
exclude
排除某些路由不应用中间件
功能中间件
函数方式中间件的实现
import { Request, Response, NextFunction } from 'express';
export function logger(req: Request, res: Response, next: NextFunction) {
console.log(`Request...`);
next();
};
全局中间件
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
app.use(logger);
await app.listen(3000);
或者 AppModule 下
consumer
.apply(logger)
.forRoutes('*') // 全局路由
ExceptionFilter
Nest设有 全局异常过滤器 前置过滤出应用中所有未处理的异常(HttpException类)
除此之外的异常(InternalServerErrorException类)始终返回JSON:
{
"statusCode": 500,
"message": "Internal server error"
}
抛出异常
new HttpException(response, status) 参数
response:响应正文JSON
status:响应HTTP状态码
import { Post, Body, HttpException, HttpStatus } from '@nestjs/common';
@Post('update/:id')
updateArticle(@Body() updateArticleDTO: UpdateArticleDTO) {
throw new HttpException('Forbidden', HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN)
}
默认响应正文JSON结构为
statusCode:默认为status提供的HTTP状态码
message:response字符串值;当值类型为对象,将覆盖整个响应JSON
可选第三个 options 参数描述错误原因,常用于记录:
try{ ... }
catch(err){
throw new HttpException(response, status, { cause: error })
}
内置异常
BadRequestExceptionUnauthorizedExceptionNotFoundExceptionForbiddenExceptionNotAcceptableExceptionRequestTimeoutExceptionConflictExceptionGoneExceptionHttpVersionNotSupportedExceptionPayloadTooLargeExceptionUnsupportedMediaTypeExceptionUnprocessableEntityExceptionInternalServerErrorExceptionNotImplementedExceptionImATeapotExceptionMethodNotAllowedExceptionBadGatewayExceptionServiceUnavailableExceptionGatewayTimeoutExceptionPreconditionFailedException
所有内置异常支持 response 和 options 参数
throw new BadRequestException('Something bad happened', { cause: new Error(), description: 'Some error description' })
自定义异常
自定义继承自 HttpException 类异常,创建异常层次结构
export class ForbiddenException extends HttpException {
constructor() {
super('Forbidden', HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN);
}
}
import ForbiddenException from '*/ForbiddenException'
@Get()
async findAll() {
throw new ForbiddenException();
}
自定义异常过滤器
通过自定义过滤器,在异常层捕获抛出的异常进行控制处理;如日志记录或不同JSON模式
新增捕获 HttpException 类异常的过滤器:
// http.exception.filter.ts
import { ExceptionFilter, Catch, ArgumentsHost, HttpException } from "@nestjs/common"
import { Request, Response } from "express";
@Catch(HttpException) // 捕获 HttpException 类型
export class HttpExceptionFilter implements ExceptionFilter {
catch(exception: HttpException, host: ArgumentsHost) {
const ctx = host.switchToHttp();
const response = ctx.getResponse<Response>();
const request = ctx.getRequest<Request>();
const status = exception.getStatus();
const message = exception.getResponse();
response
.status(status)
.json({
code: status,
message,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
path: request.url
})
}
}
@Catch()
@Catch() 装饰器将所需原数据绑定到异常过滤器,告知Nest该过滤器寻找HttpException类型异常,支持逗号分隔列表实现多种类型
ExceptionFilter
catch方法参数包含exception(当前捕获的异常对象),host(参数主机)(ArgumentsHost对象)
ArgumentsHost在HTTP 服务器,微服务和 WebSockets等提供执行上下文
绑定过滤器
绑定到Controller
import { Post, Body, ForbiddenException, UseFilters } from '@nestjs/common';
// 应用整个控制器作用域
@Controller('article')
@UseFilters(new HttpExceptionFilter())
export class ArticleController {
....
}
// 应用单个路由处理
@Post('delete/:id')
@UseFilters(new HttpExceptionFilter())
deleteArticle(@Body() updateArticleDTO: UpdateArticleDTO) {
throw new ForbiddenException();
}
@UseFilters 装饰器使用若干装饰器实例,以逗号分割
绑定到全局应用
// main.ts
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
app.UseGlobalFilters(new HttpExceptionFilters());
await app.listen(3000);
}
bootstrap();
捕获所有异常
import {
ExceptionFilter,
Catch,
ArgumentsHost,
HttpException,
HttpStatus,
} from '@nestjs/common';
import { HttpAdapterHost } from '@nestjs/core';
@Catch()
export class AllExceptionsFilter implements ExceptionFilter {
constructor(private readonly httpAdapterHost: HttpAdapterHost) {}
catch(exception: unknown, host: ArgumentsHost): void {
const { httpAdapter } = this.httpAdapterHost;
const ctx = host.switchToHttp();
const httpStatus =
exception instanceof HttpException
? exception.getStatus()
: HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
const responseBody = {
statusCode: httpStatus,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
path: httpAdapter.getRequestUrl(ctx.getRequest()),
};
httpAdapter.reply(ctx.getResponse(), responseBody, httpStatus);
}
}
@Catch() 未指定异常类型,实现捕获所有类型异常
exception: unknown 声明异常实例类型未知
httpAdapterHost HTTP适配器实现响应传递(不依赖任何平台)
继承异常过滤器
自定义新过滤器满足需求外,可以继承 ``BaseExceptionFilter` 基本过滤器实现只添加逻辑不额外其他处理
import { Catch, ArgumentsHost } from '@nestjs/common';
import { BaseExceptionFilter } from '@nestjs/core';
@Catch()
export class AllExceptionsFilter extends BaseExceptionFilter {
catch(exception: unknown, host: ArgumentsHost) {
super.catch(exception, host);
}
}
绑定基本过滤器
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
const { httpAdapter } = app.get(HttpAdapterHost);
app.useGlobalFilters(new AllExceptionsFilter(httpAdapter));
await app.listen(3000);
}
bootstrap();
Pipe
基于 @Injectable(),PipeTransform Interface实现
管道最典型的用例:
-
transformation:输入数据再转为正确格式
-
validation:验证输入数据并做出反应
值得注意这两种管道运行在Controller的路由处理器的 arguments,它们接受方法的参数,并进行操作后才会调用路由处理
内置管道
@nestjs/common 内置管道如下:
ValidationPipeParseIntPipeParseFloatPipeParseBoolPipeParseArrayPipeParseUUIDPipeParseEnumPipeDefaultValuePipe提供参数默认值ParseFilePipe
绑定管道
以 *Parse 种类管道的 ParseIntPipe 为例
@Post('update/:id')
updateArticle(@Param('id', ParseIntPipe) id: Number, @Body() updateArticleDTO: UpdateArticleDTO) {
return { id, updateArticleDTO };
}
如果路由参数 :id 为转整数无效值,将在路由处理前由管道抛出异常
自定义管道行为
除了如上 Pipe 类 ParseIntPip 依赖注入的方式,还可以通过 Pipe 类实例自定义管道选项控制管道行为
@Post('update/:id')
updateArticle(
// HttpStatus.NOT_ACCEPTABLE: 406
@Param('id', new ParseIntPipe({ errorHttpStatusCode: HttpStatus.NOT_ACCEPTABLE })) id: Number,
@Body() updateArticleDTO: UpdateArticleDTO
) {
return { id, updateArticleDTO };
}
定制管道
管道基本结构
// validation.pipe.ts
import { Injectable, PipeTransform, ArgumentMetadata } from "@nestjs/common";
@Injectable()
export class ValidationPipe implements PipeTransform {
transform(value: any, argumentMetadata: ArgumentMetadata){
return value; // pipe只有引发异常/返回原值2种情况
}
}
其中 transform 约定输入输出实现,参数:
value 当前处理方法得到的参数
metadata 处理方法参数的元数据,如路由处理参数的元数据描述,即:
interface ArgumentMetadata {
type: 'body' | 'query' | 'param' | 'custom'; // 参数源类别
metatype?: Type<unknown>; // 参数值类型, @Body() article: Article
data?: string; // 传递给装饰器值,如 @Body('id', ValidationPipe)
}
对象模式验证
实现路由参数的验证,可以定义中间件 或 委托Validator类实现,但存在 具体执行上下文问题 和 不够DRY问题,pipe提出并支持基于对象模式验证(可复用的)
基于Zod
安装:npm i -S zod
使用Zod创建应用级基于模式验证的验证管道,结构如下:
// zodValidation.pipe.ts
import { PipeTransform, ArgumentMetadata, BadRequestException } from "@nestjs/common";
import { ZodObject } from "zod";
// 后续通过@UsePipes使用,此处无需@Injectable
export class ZodValidation implements PipeTransform {
constructor(private schema: ZodObject<any>){} // 注入 传入的schema
transform(value: any, metadata: ArgumentMetadata) {
try {
this.schema.parse(value); // 基于schema对value验证
} catch (error) {
// 控制管道抛出的异常,甚至能根据error为异常添加详细信息
throw new BadRequestException('Validation failed');
}
return value;
}
}
绑定验证管道
定义schema(Zod)
// update-article.dto.ts
import { z } from 'zod';
export const updateArticleSchema = z
.object({
id: z.number(),
name: z.string().optional(),
author: z.string().optional(),
pageTotal: z.number().optional()
})
// 顺手生成 DTO 类型
export type UpdateArticleDTO = z.infer<typeof updateArticleSchema>
创建管道验证实例并绑定
@Post('update')
// @UsePipes 传入基于指定schema的Zod验证管道实例
@UsePipes(new ZodValidationPipe(updateArticleSchema))
updateArticle(
@Body() updateArticleDTO: UpdateArticleDTO // 标注参数类型
) {
return updateArticleDTO;
}
注:zod 库需要在 tsconfig.json 文件中启用 strictNullChecks 配置。
基于装饰器的类验证
安装:npm i -S class-validator class-transformer
定义DTO类
// update-article.dto.ts
import { IsString, IsInt } from 'class-validator';
export class UpdateArticleDTO {
@IsInt()
id: number;
@IsString()
name: string;
@IsString()
author: string;
@IsInt()
pageTotal: number;
}
验证管道类
// validation.pipe.ts
import { PipeTransform, Injectable, ArgumentMetadata, BadRequestException } from '@nestjs/common';
import { validate } from 'class-validator';
import { plainToInstance } from 'class-transformer';
@Injectable()
export class ValidationPipe implements PipeTransform<any> {
async transform(value: any, { metatype }: ArgumentMetadata) {
if (!metatype || !this.toValidate(metatype)) {
return value;
}
const object = plainToInstance(metatype, value);
const errors = await validate(object);
if (errors.length > 0) {
throw new BadRequestException('Validation failed');
}
return value;
}
private toValidate(metatype: Function): boolean {
const types: Function[] = [String, Boolean, Number, Array, Object];
return !types.includes(metatype);
}
}
实例化并绑定
@Post()
async update(
@Body(new ValidationPipe()) updateCatDto: UpdateArticleDTO,
) {
this.articleService.update(updateCatDto);
}
全局作用域管道
就像Filter、Middleware,app.useGlobalPipes支持通过
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
app.useGlobalPipes(new ValidationPipe());
await app.listen(3000);
}
bootstrap();
Guard
基于 @Injectable(),CanActivate Interface实现
支持请求/响应的正确位置插入声明的逻辑,执行于所有中间件之后、管道/拦截器之前
守卫遵循单一职责single single responsibility,如鉴权守卫、身份验证守卫
授权守卫
以简单的 authorization 为例
import { Injectable, CanActivate, ExecutionContext } from "@nestjs/common";
@Injectable()
export class AuthGuard implements CanActivate {
canActivate(context: ExecutionContext):boolean | Promise<boolean> {
const request = context.switchToHttp().getRequest();
// other handle
return true;
}
}
canActivate
守卫的 canActivate 是必须的,它要求返回一个布尔值或异步返回的布尔值,return false将拒绝请求,守卫默认抛出 ForbiddenException 异常
ExecutionContext 作为唯一参数,它继承自 ArgumentHosts,提供获取执行上下文
绑定守卫
绑定到Controller
@Controller('article')
@UseFilters(new HttpExceptionFilter())
@UseGuards(AuthGuard)
export class ArticleController { }
同样支持绑定到具体路由或者全局,如:
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
app.useGlobalGuards(new RolesGuard()); // 同样允许传递实例
自定义元数据
通过自定义metadata 配合 执行上下文(ExecutionContext)实现基于角色的身份验证
// roles.decorator.ts
import { Reflector } from "@nestjs/core";
export const Roles = Reflector.createDecorator<string[]>(); // 接受 string[] 类型
NestJs支持通过 #Reflector.createDerector 创建装饰器或 @SetMetadata 装饰器自定义元数据到路由
注释处理程序
@Controller('article')
@UseFilters(new HttpExceptionFilter())
@UseGuards(AuthGuard)
export class ArticleController {
constructor(private readonly articleService: ArticleService) {}
@Roles(['admin']) // 注释角色
@Get('all')
async getArticles(): Promise<Array<Article>> {
return await this.articleService.getArticles();
}
}
访问元数据
import {Reflector} from "@nestjs/core";
import { Injectable, CanActivate, ExecutionContext, UnauthorizedException } from "@nestjs/common";
import {Roles} from '../decorators/roles.decorator'
@Injectable()
export class RolesGuard implements CanActivate {
constructor(private reflector: Reflector){} // IoC控制反转
canActivate(context: ExecutionContext): boolean | Promise<boolean> {
// 访问元数据
const roles = this.reflector.get(Roles, context.getHandler());
if(!roles) return true; // 未注释有效Roles,即无角色条件
const request = context.switchToHttp().g etRequest();
const user = request.user; // 取出用户
throw new UnauthorizedException();
// return matchRoles(roles, user.roles);
}
}
Interceptor
基于 @Injectable(),NestInterceptor Interface实现
拦截器面向切面设计(AOP),作用包括:
- 在方法执行之前/之后绑定额外的逻辑
- 转换函数返回的结果
- 转换函数抛出的异常
- 扩展基本功能行为
- 根据特定条件完全覆盖函数(例如,出于缓存目的)
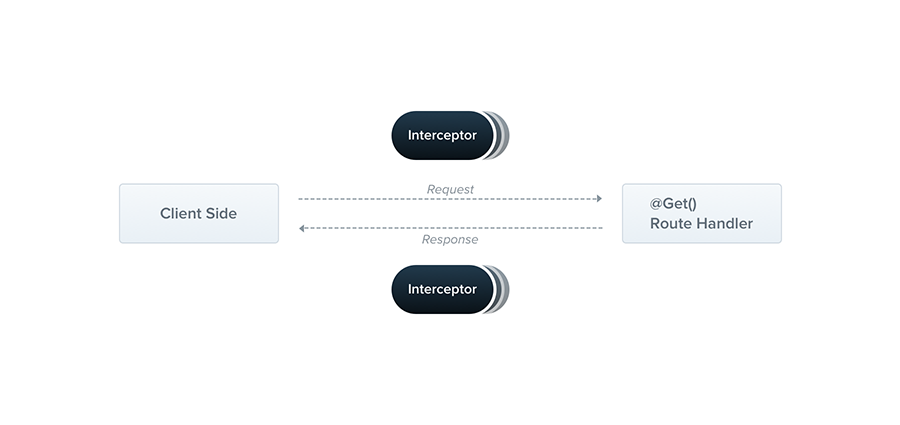
切面拦截
// logging.interceptor.ts
import { Injectable, NestInterceptor, ExecutionContext, CallHandler } from "@nestjs/common";
import { Observable, tap } from "rxjs";
@Injectable()
export class LoggingInterceptor implements NestInterceptor {
intercept(context: ExecutionContext, next: CallHandler<any>): Observable<any> {
// 路由处理前
console.log('Before...');
const now = Date.now();
return next
.handle() // 路由处理后
.pipe(
tap(() => console.log(`After... ${Date.now() - now}ms`))
)
}
}
intercept
拦截器的 intercept 是必须的,同样能够接收ExecutionContext参数获取执行上下文;
另一个参数 CallHander ,实现了 handle() 方法,它返回 RxJs 的 Observable 类型值(意味着拦截器正常情况必须返回流)。我们以调用 handle 作为切入点插入附加逻辑;未调用 handle 即不执行路由处理
绑定Interceptor
绑定到 Controller
@Controller('article')
@UseGuards(AuthGuard)
@UseGuards(RolesGuard)
@UseInterceptors(LoggingInterceptor)
@UseFilters(new HttpExceptionFilter())
export class ArticleController { }
同样支持绑定到具体路由,以及全局绑定
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
app.useGlobalInterceptors(new LoggingInterceptor());
响应映射
// transform.interceptor.ts
import { Injectable, NestInterceptor, ExecutionContext, CallHandler } from "@nestjs/common";
import { Observable, map } from "rxjs";
export interface Response<T> {
data: T;
code: number;
message: string;
}
@Injectable()
// NestInterceptor<T, R> ,其中 T 表示 Observable<T>(支持响应流)的类型,R 是 Observable<R> 封装值的类型。
export class transformInterceptor<T> implements NestInterceptor<T, Response<T>> {
intercept(context: ExecutionContext, next: CallHandler<any>): Observable<Response<T>> {
return next
.handle()
.pipe(
map(data => ({
data,
code: 200,
message: 'success'
}))
)
}
}
异常映射
// error.interceptor.ts
import {
Injectable,
NestInterceptor,
ExecutionContext,
BadGatewayException,
CallHandler,
} from '@nestjs/common';
import { Observable, throwError } from 'rxjs';
import { catchError } from 'rxjs/operators';
@Injectable()
export class ErrorsInterceptor implements NestInterceptor {
intercept(context: ExecutionContext, next: CallHandler): Observable<any> {
return next
.handle()
.pipe(
catchError(err => throwError(() => new BadGatewayException())),
);
}
}
覆盖流
import { Injectable, NestInterceptor, ExecutionContext, CallHandler } from '@nestjs/common';
import { Observable, of } from 'rxjs';
@Injectable()
export class CacheInterceptor implements NestInterceptor {
intercept(context: ExecutionContext, next: CallHandler): Observable<any> {
const isCached = true;
if (isCached) {
return of([]); // 自定义返回流
}
return next.handle();
}
}
配合 RxJS 的操作符,如 timeout 等实现更多对流的操纵与逻辑控制
自定义路由装饰器
Nest围绕装饰器语言特性构建
参数装饰器
即与 HTTP 理由处理程序使用,如内置参数装饰器:
@Request(), @Req() |
req |
|---|---|
@Response(), @Res() |
res |
@Next() |
next |
@Session() |
req.session |
@Param(param?: string) |
req.params / req.params[param] |
@Body(param?: string) |
req.body / req.body[param] |
@Query(param?: string) |
req.query / req.query[param] |
@Headers(param?: string) |
req.headers / req.headers[param] |
@Ip() |
req.ip |
@HostParam() |
req.hosts |
通过自定义路由装饰器,能更好访问参数
// user.decorator.ts
import {createParamDecorator, ExecutionContext} from '@nestjs/common';
export const User = createParamDecorator((data: any, ctx: ExecutionContext) => {
const request = ctx.switchToHttp().getRequest();
return request.user;
})
传递数据
data 参数支持向装饰器传递数据作为条件,如支持访问用户实体特定属性
// user.decorator.ts
import {createParamDecorator, ExecutionContext} from '@nestjs/common';
export const User = createParamDecorator((data: string, ctx: ExecutionContext) => {
const request = ctx.switchToHttp().getRequest();
const user = request.user;
return data ? user?.[data] : user;
})
路由参数中使用
@Get()
async findOne(@User() user: UserEntity) {
console.log(user;)
}
@Get()
async findUsername(@User('username') username: string) {
console.log(username)
}
支持管道
与内置参数装饰器一样,但需 pipe 配置 validateCustomDecorators 开启验证
@Get()
async findOne(
@User(new ValidationPipe({ validateCustomDecorators: true }))
user: UserEntity,
) {
console.log(user);
}
@Get()
async findUsername(
@User('username', new ValidationPipe({ validateCustomDecorators: true }))
username: string,
) {
console.log(username);
}
组成的装饰器
Nest 提供 applyDecorators 将多个装饰器组合
// auth.decorator.ts
import { SetMetadata, UseGuards, applyDecorators, UseFilters } from "@nestjs/common"
import { AuthGuard } from "src/guards/auth.guard"
import { HttpExceptionFilter } from "src/filters/exception.filter"
import { ApiBearerAuth } from "@nestjs/swagger"
export const Auth = function (...Roles: string[]){
applyDecorators(
SetMetadata('roles', Roles),
UseGuards(AuthGuard),
ApiBearerAuth(),
UseFilters(HttpExceptionFilter),
)
}